Note
Go to the end to download the full example code.
Graphene hv scan¶
Simple workflow for analyzing a photon energy scan data of graphene as simulated from a third nearest neighbor tight binding model. The same workflow can be applied to any photon energy scan.
Import the “fundamental” python libraries for a generic data analysis:
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
Instead of loading the file as for example:
# from navarp.utils import navfile
# file_name = r"nxarpes_simulated_cone.nxs"
# entry = navfile.load(file_name)
Here we build the simulated graphene signal with a dedicated function defined just for this purpose:
from navarp.extras.simulation import get_tbgraphene_hv
entry = get_tbgraphene_hv(
scans=np.arange(90, 150, 2),
angles=np.linspace(-7, 7, 300),
ebins=np.linspace(-3.3, 0.4, 450),
tht_an=-18,
)
Plot a single analyzer image at scan = 90¶
First I have to extract the isoscan from the entry, so I use the isoscan method of entry:
iso0 = entry.isoscan(scan=90)
Then to plot it using the ‘show’ method of the extracted iso0:
iso0.show(yname='ekin')
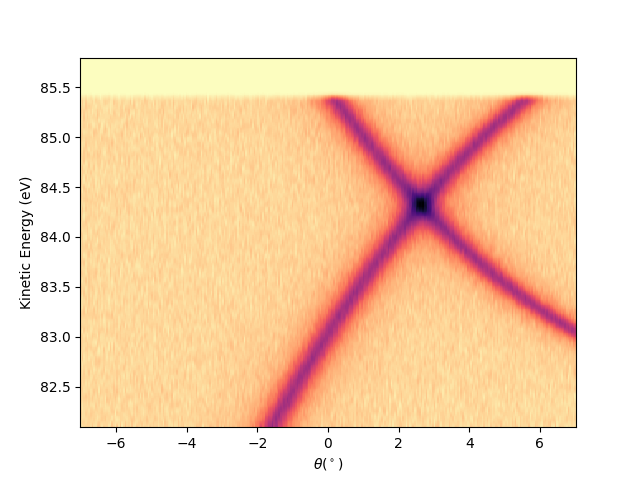
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh object at 0x78b8ea88ca90>
Or by string concatenation, directly as:
entry.isoscan(scan=90).show(yname='ekin')
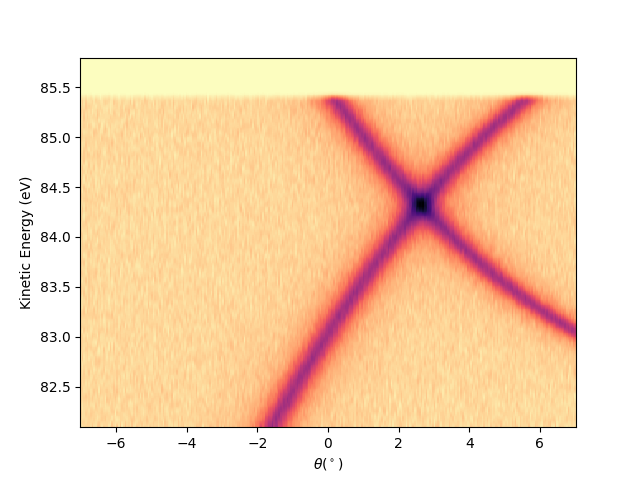
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh object at 0x78b8ea946dd0>
Fermi level determination¶
The initial guess for the binding energy is: ebins = ekins - (hv - work_fun). However, the better way is to proper set the Fermi level first and then derives everything form it. In this case the Fermi level kinetic energy is changing along the scan since it is a photon energy scan. So to set the Fermi level I have to give an array of values corresponding to each photon energy. By definition I can give:
efermis = entry.hv - entry.analyzer.work_fun
entry.set_efermi(efermis)
Or I can use a method for its detection, but in this case, it is important to give a proper energy range for each photon energy. For example for each photon a good range is within 0.4 eV around the photon energy minus the analyzer work function:
energy_range = (
(entry.hv[:, None] - entry.analyzer.work_fun) +
np.array([-0.4, 0.4])[None, :])
entry.autoset_efermi(energy_range=energy_range)
scan(eV) efermi(eV) FWHM(meV) new hv(eV)
90.0000 85.3995 59.4 89.9995
92.0000 87.4002 58.9 92.0002
94.0000 89.4002 58.2 94.0002
96.0000 91.4004 58.5 96.0004
98.0000 93.4005 58.4 98.0005
100.0000 95.4003 58.5 100.0003
102.0000 97.4004 58.2 102.0004
104.0000 99.4003 59.1 104.0003
106.0000 101.4004 57.7 106.0004
108.0000 103.4007 57.8 108.0007
110.0000 105.4002 58.5 110.0002
112.0000 107.3998 59.5 111.9998
114.0000 109.4001 58.6 114.0001
116.0000 111.4005 57.8 116.0005
118.0000 113.4004 58.5 118.0004
120.0000 115.4009 57.7 120.0009
122.0000 117.4002 58.9 122.0002
124.0000 119.4003 58.1 124.0003
126.0000 121.4005 58.2 126.0005
128.0000 123.3998 59.2 127.9998
130.0000 125.4005 58.3 130.0005
132.0000 127.4004 58.4 132.0004
134.0000 129.4006 58.2 134.0006
136.0000 131.4005 57.7 136.0005
138.0000 133.4008 59.5 138.0008
140.0000 135.4007 57.1 140.0007
142.0000 137.3999 59.0 141.9999
144.0000 139.4001 59.9 144.0001
146.0000 141.3996 60.5 145.9996
148.0000 143.4001 59.2 148.0001
In both cases the binding energy and the photon energy will be updated consistently. Note that the work function depends on the beamline or laboratory. If not specified is 4.5 eV.
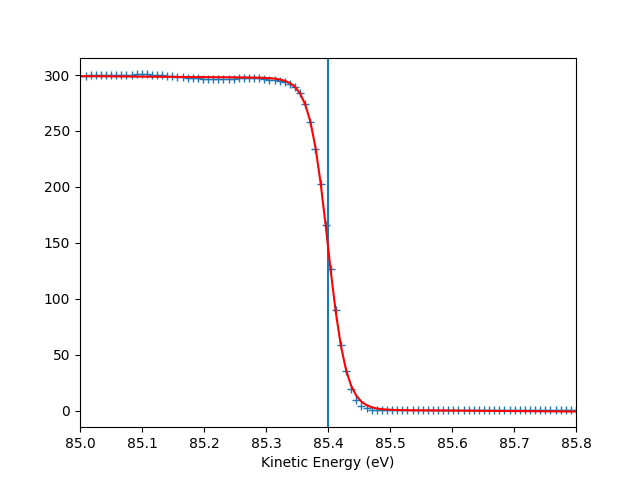
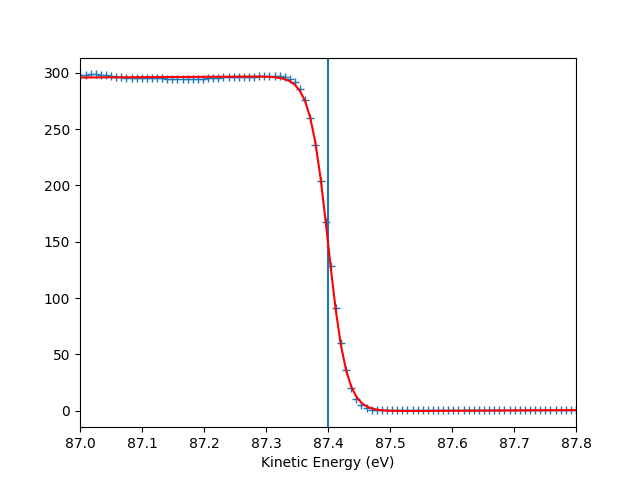
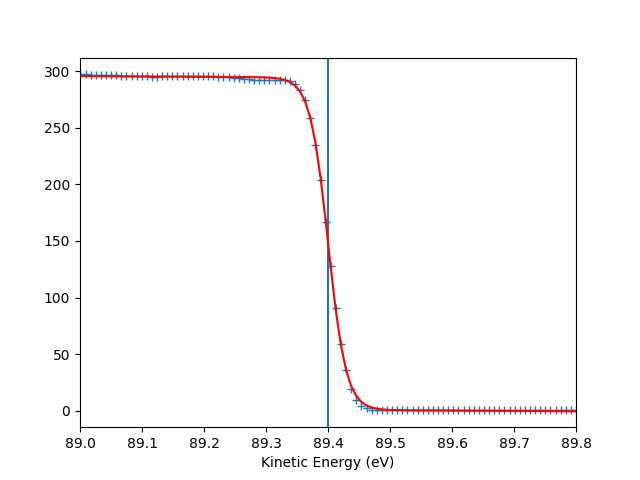
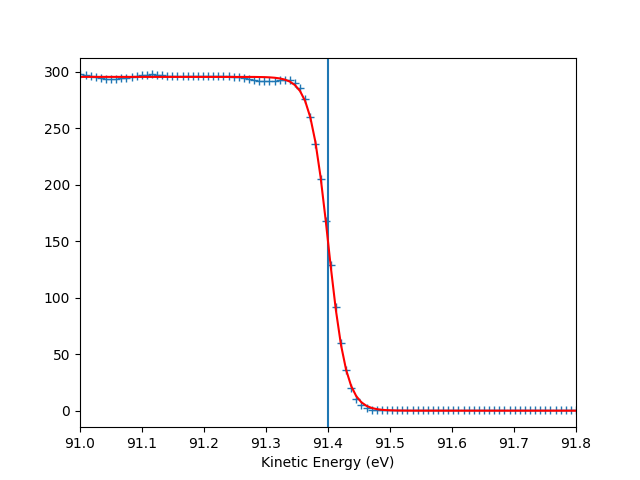
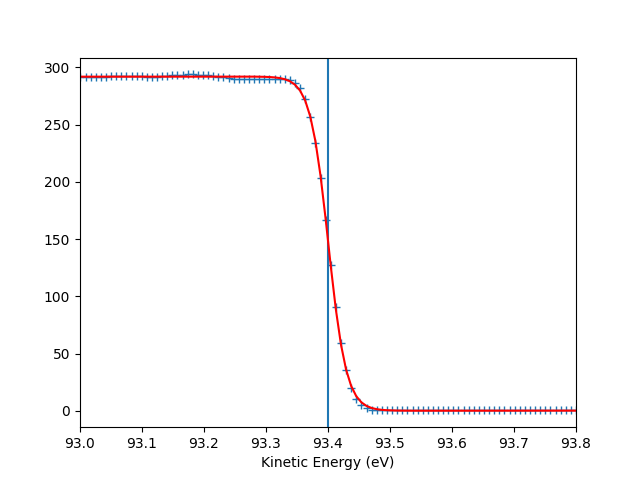
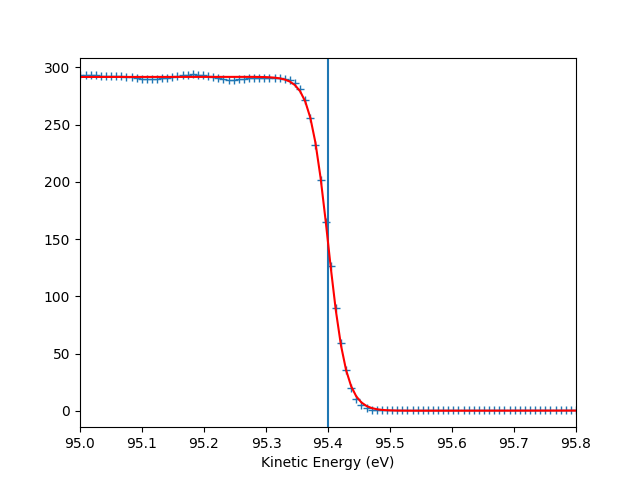
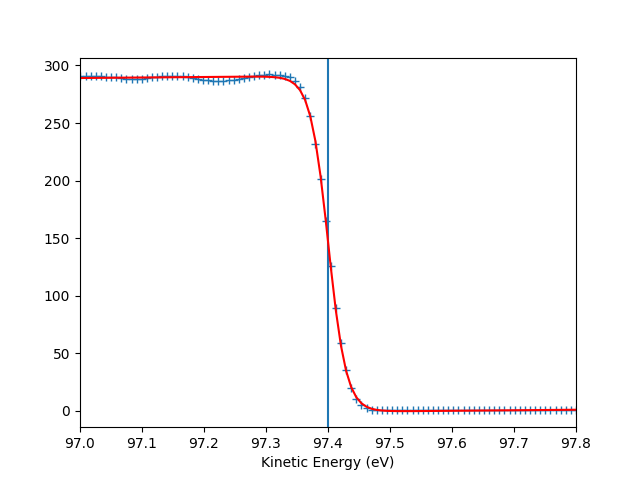
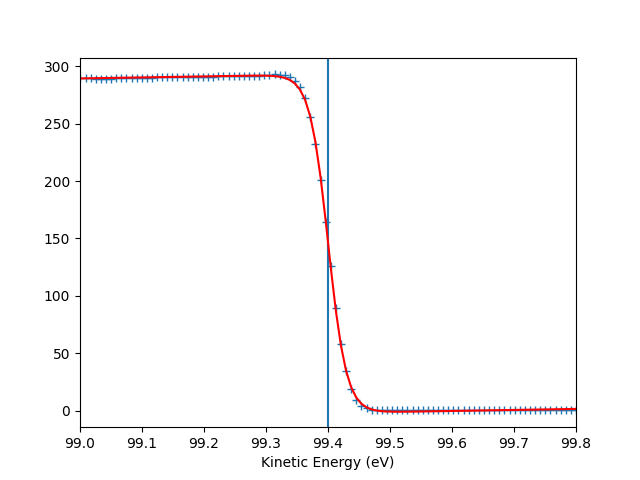
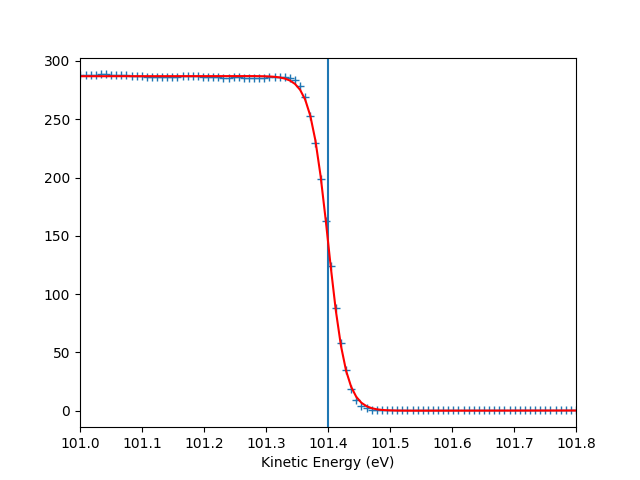
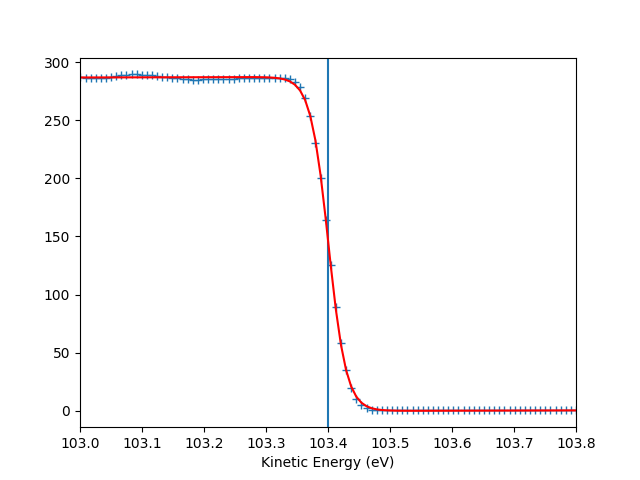
To check the Fermi level detection I can have a look on each photon energy. Here I show only the first 10 photon energies:
for scan_i in range(10):
print("hv = {} eV, E_F = {:.0f} eV, Res = {:.0f} meV".format(
entry.hv[scan_i],
entry.efermi[scan_i],
entry.efermi_fwhm[scan_i]*1000
))
entry.plt_efermi_fit(scan_i=scan_i)
hv = 89.99952201750287 eV, E_F = 85 eV, Res = 59 meV
hv = 92.0001973948537 eV, E_F = 87 eV, Res = 59 meV
hv = 94.00020032410666 eV, E_F = 89 eV, Res = 58 meV
hv = 96.00041349960748 eV, E_F = 91 eV, Res = 58 meV
hv = 98.00053087039018 eV, E_F = 93 eV, Res = 58 meV
hv = 100.000260514306 eV, E_F = 95 eV, Res = 59 meV
hv = 102.00044025669692 eV, E_F = 97 eV, Res = 58 meV
hv = 104.0002712950043 eV, E_F = 99 eV, Res = 59 meV
hv = 106.00036106751848 eV, E_F = 101 eV, Res = 58 meV
hv = 108.00067351202694 eV, E_F = 103 eV, Res = 58 meV
Plot a single analyzer image at scan = 110 with the Fermi level aligned¶
entry.isoscan(scan=110).show(yname='eef')
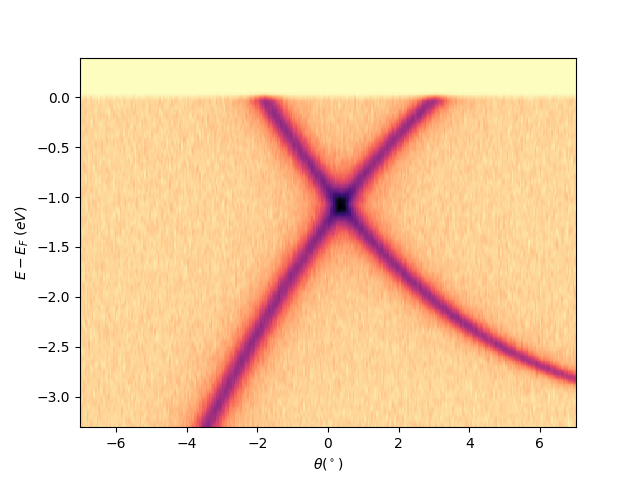
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh object at 0x78b8ea2b8e80>
Plotting iso-energetic cut at ekin = efermi¶
entry.isoenergy(0).show()
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh object at 0x78b8ea345180>
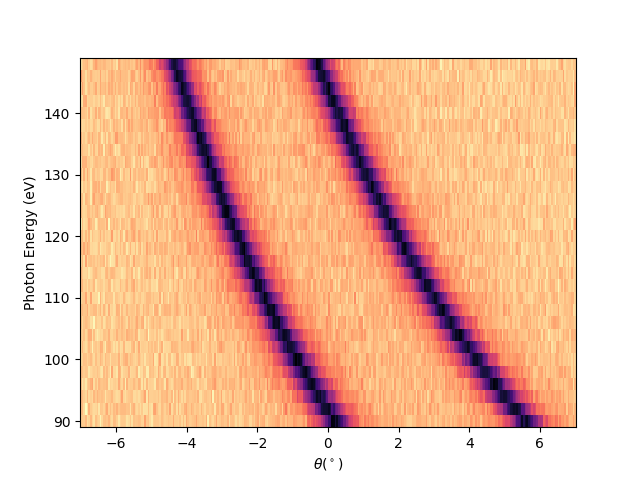
Plotting in the reciprocal space (k-space)¶
I have to define first the reference point to be used for the transformation. Meaning a point in the angular space which I know it correspond to a particular point in the k-space. In this case the graphene Dirac-point is for hv = 120 is at ekin = 114.3 eV and tht_p = -0.6 (see the figure below), which in the k-space has to correspond to kx = 1.7.
hv_p = 120
entry.isoscan(scan=hv_p, dscan=0).show(yname='ekin', cmap='cividis')
tht_p = -0.6
e_kin_p = 114.3
plt.axvline(tht_p, color='w')
plt.axhline(e_kin_p, color='w')
entry.set_kspace(
tht_p=tht_p,
k_along_slit_p=1.7,
scan_p=0,
ks_p=0,
e_kin_p=e_kin_p,
inn_pot=14,
p_hv=True,
hv_p=hv_p,
)
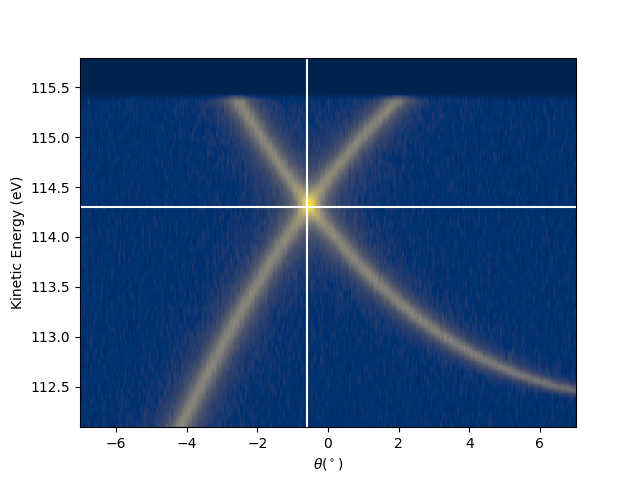
tht_an = -18.040
scan_type = hv
inn_pot = 14.000
phi_an = 0.000
k_perp_slit_for_kz = 0.000
kspace transformation ready
Once it is set, all the isoscan or iscoenergy extracted from the entry will now get their proper k-space scales:
entry.isoscan(120).show()
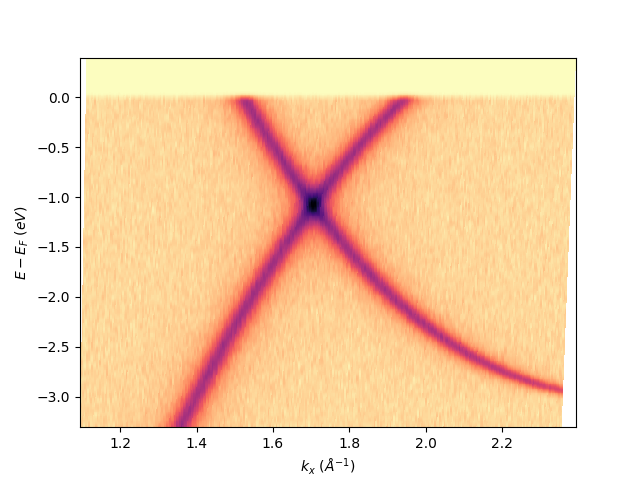
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh object at 0x78b8ea0ff490>
sphinx_gallery_thumbnail_number = 17
entry.isoenergy(0).show(cmap='cividis')
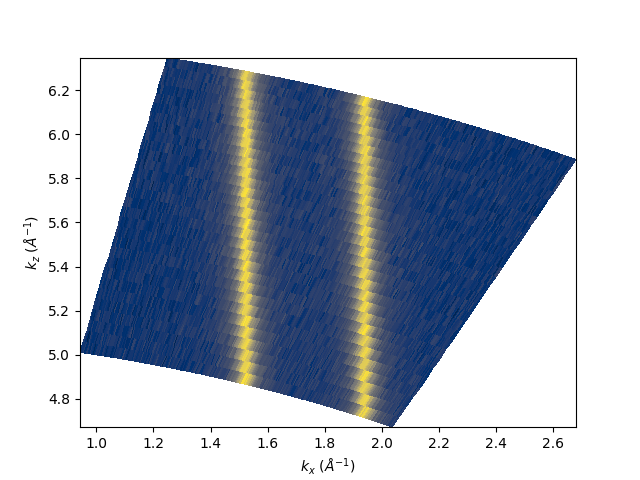
<matplotlib.collections.QuadMesh object at 0x78b8e9f8e050>
I can also place together in a single figure different images:
fig, axs = plt.subplots(1, 2)
entry.isoscan(120).show(ax=axs[0])
entry.isoenergy(-0.9).show(ax=axs[1])
plt.tight_layout()
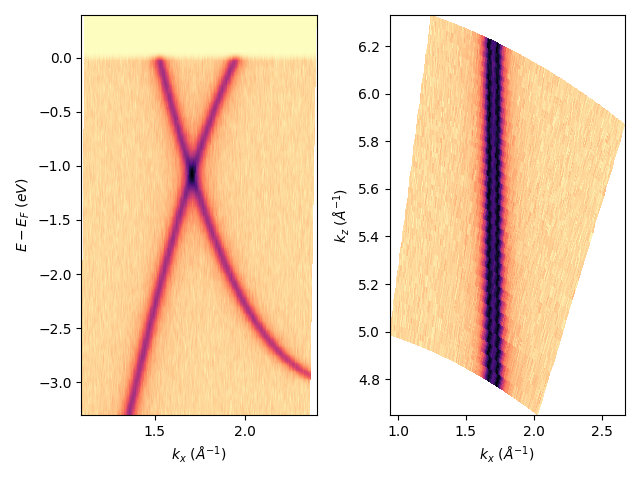
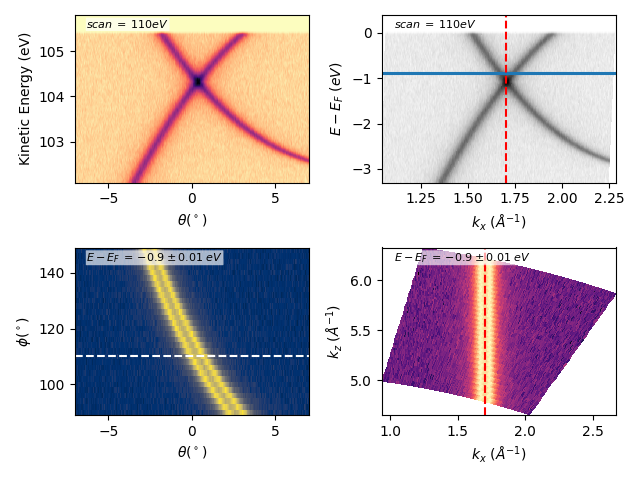
Many other options:¶
fig, axs = plt.subplots(2, 2)
scan = 110
dscan = 0
ebin = -0.9
debin = 0.01
entry.isoscan(scan, dscan).show(ax=axs[0][0], xname='tht', yname='ekin')
entry.isoscan(scan, dscan).show(ax=axs[0][1], cmap='binary')
axs[0][1].axhline(ebin-debin)
axs[0][1].axhline(ebin+debin)
entry.isoenergy(ebin, debin).show(
ax=axs[1][0], xname='tht', yname='phi', cmap='cividis')
entry.isoenergy(ebin, debin).show(
ax=axs[1][1], cmap='magma', cmapscale='log')
axs[1][0].axhline(scan, color='w', ls='--')
axs[0][1].axvline(1.7, color='r', ls='--')
axs[1][1].axvline(1.7, color='r', ls='--')
x_note = 0.05
y_note = 0.98
for ax in axs[0][:]:
ax.annotate(
"$scan \: = \: {} eV$".format(scan, dscan),
(x_note, y_note),
xycoords='axes fraction',
size=8, rotation=0, ha="left", va="top",
bbox=dict(
boxstyle="round", fc='w', alpha=0.65, edgecolor='None', pad=0.05
)
)
for ax in axs[1][:]:
ax.annotate(
"$E-E_F \: = \: {} \pm {} \; eV$".format(ebin, debin),
(x_note, y_note),
xycoords='axes fraction',
size=8, rotation=0, ha="left", va="top",
bbox=dict(
boxstyle="round", fc='w', alpha=0.65, edgecolor='None', pad=0.05
)
)
plt.tight_layout()
Total running time of the script: (0 minutes 3.437 seconds)